By Mr. C.C. Wang
President (TAMI)
Due to a lower market performance in 2016, the total production value of the Taiwanese plastics machinery market resulted in a valuation of NTD 40.6 billion dollars. This represents a 6.3% annual decrease compared to its previous year. Overall, the export value in 2016 reached USD 1.03 billion and decreased by 8.0%, while the import value reached USD 284.1 million and increased by 25.5%. On the same imports report, it also showed the semiconductor, information technology, communication tech industry and other high-tech industries had a minor decrease in 2014, and even dropped further in 2015 before finally returning to growth in 2016.
Based on the plastics machinery production and sales report, indications were that plastics processing and product manufacturing are still highly labor-oriented. In past years, the traditional plastics production has been outsourced and the high-tech has been fully developed, forcing the plastics processing and product manufacturing to transform and adapt to the growing precision manufacturing demand. In other words, the need for automated machinery is increasing while the need for traditional machinery is decreasing. The export percentage over the total production value in the past also shows that the exports amounted to 62% in 1992, 75% in 1995, and had increased to 82% in 2015 and 2016. Industry critics pointed out that the export percentage would only increase slightly in the future. Taking into account all local purchases, imports account for the same as those locally produced, while the high-end machinery still relies mostly on imports. Because of this situation, it is worthwhile for the plastics machinery industry to rethink their strategy for the future.
Most of the Taiwanese plastics machinery producers are small and medium enterprises, totaling approximately 280 companies. Among these companies, roughly 98% are small and medium enterprises, and 90% of them are clustered in Tainan, Taichung, and Hsinchu and represent an iconic industry in the region. In the early days, many employees had learned professional skills and established their own businesses later, and their supply chains were very similar to each other. This increase in similar manufacturing has led to even more fierce competition in Taiwan. As a possible solution to this problem, it is expected that the industry can integrate and distinguish their products, setting clear differences between functions and markets, and enhance their services and production quality. But jumping out from behind price competition also means less direct competition between each of Taiwan's manufacturers. Integrating the industry is the key factor for achieving such a goal.
1. TAIWAN PLASTIC MACHINERY STATUS
The production had dramatically increased by 50% in 2010. In 2011, the production value reached NTD 47.9 billion and increased 6.4%; in 2012, the production value reached NTD 48.6 billion and increased 1.6%; in 2013, the value reached NTD 45.6 billion and decreased 6.1%; in 2016, the value reached NTD 40.6 billion and decreased 6.3%. On average, among all 280 manufacturers, the current annual revenue among each manufacturer is NTD 140 million, which has doubled compared to the average value of NTD 80 million in overall manufacturing. For more plastic machinery production value, see table (1).
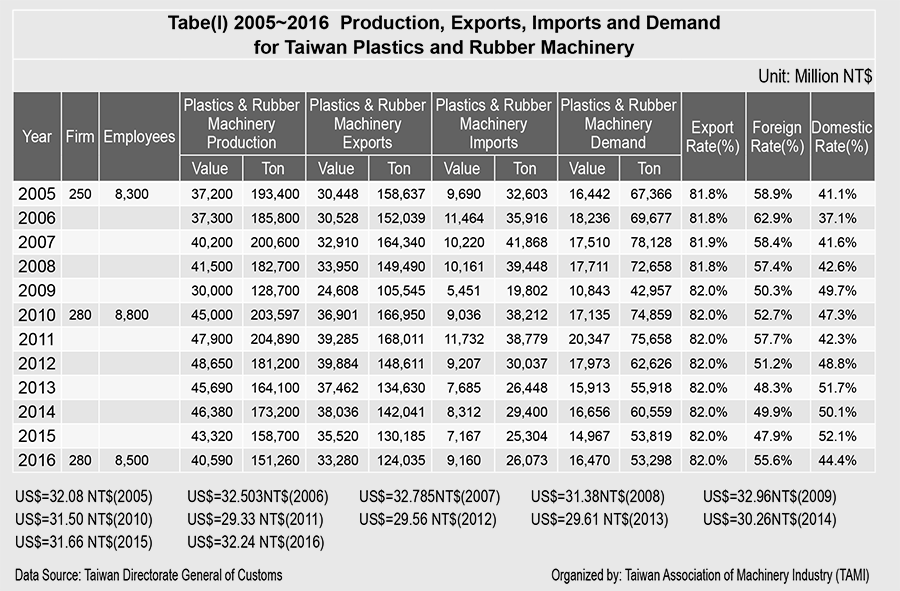
When value is categorized by product type, the injection molding industry accounts for the largest for both production amount and value. Their major exporting countries are China and Hong Kong, Vietnam, India, Thailand, Indonesia, USA, Turkey, and Malaysia. The second largest industry is extrusion-molding machinery, the third is blow molding, and the rest in the sequence are vacuum forming, thermoforming, tire-making machinery, and other custom-made machinery.
2. EXPORT STATUS OF TAIWAN PLASTIC MACHINERY
Based on the import and export report prepared by the customs office, Taiwanese plastics machinery exports have remained stable with limited changes in the past 5 years. The total export value was USD 1.17 billion in 2010, USD 1.34 billion in 2011, USD 1.35 billion in 2012, USD 1.26 billion in both 2013 and 2014, USD 1.12 billion in 2015, and USD 1.03 billion in 2016. The detailed information is shown as the following:
2.1 By Product Types
Among all plastics machinery exports in 2016, the customs office has organized a category of other plastics machinery and it was listed at the top in exports, with a total value of USD 289.4 million, decreased 10%, and accounted for 28.0% of over all exports in 2016. The second largest product category in exports was injection molding, with total value of USD 264.4 million, 5,761 machines sold, decreased 9.2%, and accounted 25.6% over all export. The third was extrusion machinery, with total value of USD 112.7 million, 1,542 machines sold, and accounted 10.9%. The fourth was blow molding machinery, with total value of USD 86.9 million, 917 machines sold, and accounted 8.4%. The fifth was vacuum and thermoforming machinery, with a total value of USD 68.3 million, 1,742 machines sold, and accounted 6.6%. The rest is sequence were other molding making and type making machinery.
2.2 By Export Destination
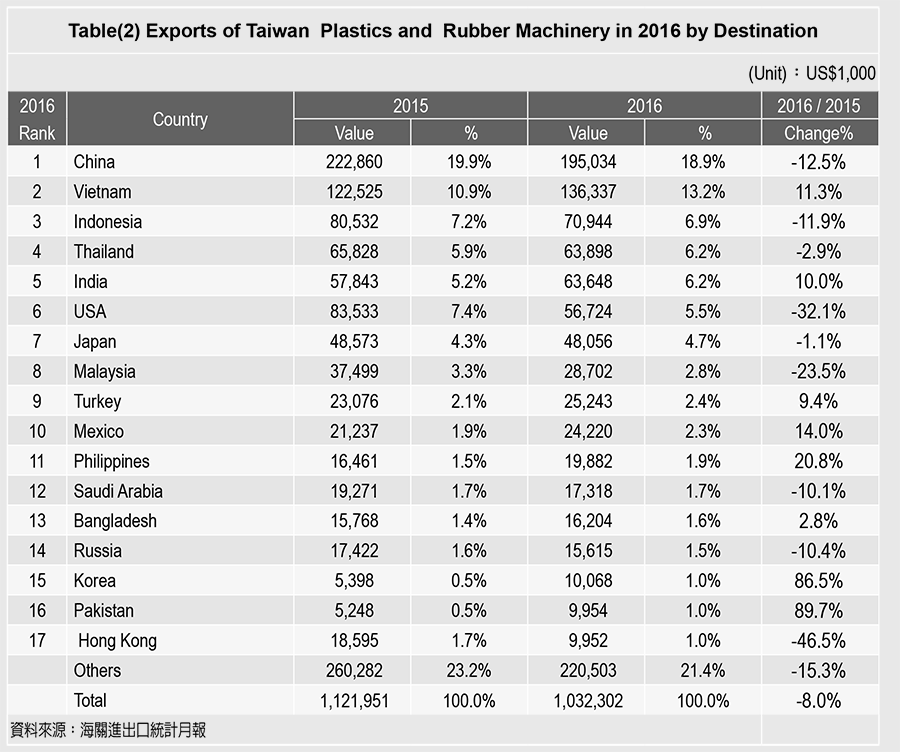
In 2016, the top export destination for Taiwanese exports was China, with total value of USD 195 million, decreased 12.5%, and accounted for 18% of over all exports. The second largest destination was Vietnam, with total value of USD 136.3 million, increased 1.3%, and accounted for 13.2% over all exports. The third was Indonesia, with total value of USD 70.9 million, decreased 11.9%, and accounted for 6.9% of over all exports.
The rest for export destination ranking were in sequence as Thailand 6.2%, India 6.2%, USA 5.5%, Japan 4.7%, Malaysia 2.8%, Turkey 2.4%, and Mexico 2.3%. The top 10 export destinations account for 70% of all exports.
By categorizing the exports into regions, this also shows that Asia and North America are still the major markets for Taiwan plastics machinery exports, while Asia accounts for up to 60% and is viewed as the top market for Taiwan exports. Among all these exports, most of them are small and medium scale plastics processing and product builders. On the other hand in Europe, the local plastics making industries are the hub for traditional plastics manufacturing and have been developed with a long history; for instance, roughly 60% of both Italian and German machinery are exported locally in Europe. The numbers of Taiwan plastics machinery being exported to Europe is still comparably much less.
China, even though it is still the largest export destination for Taiwan machinery, there are many new policies and market shifts happening there. From 2005 to 2011, new policies such as macro-economy control and stricter rules on customs tax exemptions have affected Taiwan machinery exports to China; whereas China still imports many pieces of high-end machinery from Germany and Japan. In 2014, Taiwan machinery exports to China accounted for 28% of over all exports, and decreased to 20% in 2015 and 19% in 2016. For the detailed information on Taiwan export destinations, see table (2).
3. IMPORT STATUS OF TAIWAN PLASTIC MACHINERY
Taiwan plastics machinery imports have gone through some unstable fluctuations in the past 5 years. In 2010, the total value of imports reached USD 285 million, then USD 400 million in 2011, USD 310 million in 2012, USD 260 million in 2013, and the imports finally grew by 5.9% with USD 274 million in 2014. In 2015, it decreased 17.6% to USD 2.26 million, but then increased 25.5% to USD 284 million in 2016. There is more information on imports by origin and product types as follow:
3.1 By Product Types
To view the Taiwan plastics machinery industry by product types, other machinery types rank at the top with USD 96.8 million and accounted for 34.1% of over all imports. The second largest import was injection molding, where the total value was USD 58.5 million with 1,050 machines being imported and accounted for 20.6% of over all imports. The third largest import was extrusion molding with USD 28.9 million, 350 machines imported, and accounted for 10.2%. The rest in ranking were blow molding, vacuum forming and thermoforming, and tire making machinery, and etc.
3.2 By import origin
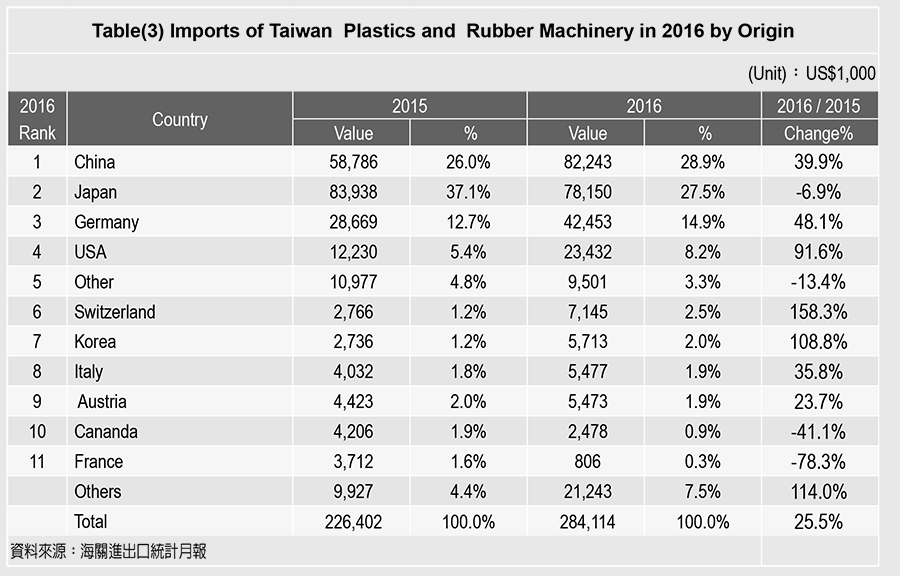
The total value of all 2016 import was USD 284.1 million. Among them, China exported USD 82.2 million and ranked at the top of the 2016 import origin for plastic machinery to Taiwan, which increased 39.9% and counted 28.9% of market share. The second largest import origin was Japan, with total value of USD 78.2 million, decreased 6.9%, and accounted for 27.5% of over all imports. The third largest origin was Germany, with a total value of USD 42.5 million and 14.9% market share. The rest in ranking were USA 8.2% and Switzerland 2.5%.
The major players for Taiwan plastics machinery 2016 imports came from China, Japan, and Germany, which amounted to 71% of over all plastics machinery imports to Taiwan. For more detailed information on Taiwan plastic machinery import origin, see table (3).
4. GLOBAL PLASTIC MACHINERY EXPORT STATUS
The largest plastics machinery producers are Germany, China, Japan, Italy, USA, Taiwan, and Korea, while Germany is the biggest producer and exporter among all of them. On the other hand, China is the largest importing and purchasing country. Other countries like Japan, Italy, USA, Taiwan, and Korea are viewed as critical suppliers for plastics machinery exports.
In 2016, Germany, China, Japan, Italy, USA, and Taiwan contributed a total of USD 15.8 billion, while the total global trade of plastic machinery was roughly USD 18.5 billion. This means that the top 6 exporters have already accounted up to 90% of plastics machinery exports globally. Aside from the top 6 countries, other iconic producers in the industry include Korea, Switzerland, Austria, Canada, France, UK, and India.
To examine the 2016 total export value from each top exporter, Germany exported near USD 5.5 billion, China exported USD 3.5 billion, Japan and Italy exported USD 2.1 billion, USA exported USD 1.6 billion, and Taiwan exported USD 1.0 billion. Comparing these exporters value from 2014 to 2016, it shows a 7.3% decrease of USD 1.3 billion.
4.1 Germany Export Status
Germany is still the leader for the plastics machinery industry worldwide, of which their trade value could count up to nearly 30% of the overall trade globally. In 2016, their export value reached nearly USD 5.5 billion and increased by 3.9% compared to the previous year. However, it still decreased by 12.4% when it was compared to its own exports in 2013.
Another point worth noticing was that the export value of Germany’s plastics machinery increased much more than the export value of China.
The top export destination for German machinery in 2016 was to the USA, which grew 7.5% to USD 850 billion and accounted 15.7% of all German plastic machinery export. The second largest destination was to China, with the value of USD 690 million, decreased 3.5%, and accounted 12.8% of all German machinery export. The third largest destination was to Mexico, with the total value of USD 283 million, largely increased by 50.9%, and accounted 5.2% of all German machinery exports.
The rest of the market share for German machinery exports were Poland 4.2% (-9.2%), France 3.9% (+12.4%), Italy 3.7% (+9.2%), India 3.7% (+31.0%), Czech Republic 3.1% (+5.6%), then UK 2.8% and Spain 2.7%.
4.2 China Export Status
China has become the largest country for plastics machinery production, import, and purchase, and their exports also jumped to ranking the second largest globally. China overall exported USD 3.5 billion worth of plastics machinery in 2016, which decreased by 0.1% compared to its previous year; however, its exports still massively exceeded the value from Japan and Italy, with most of the machinery exported focused on low to medium quality and pricing products.
The top market for China plastics machinery exports in 2016 was to Vietnam, with USD 301 million, decreased 5.0%, and accounted for 8.6% of the market share. The second largest export was to the USA, with USD 264 million, increased 24.5%, and accounted for 7.5%. The third was India, with USD 255 million, increased 33.0%, and accounted for 7.3%.
The rest of the market share for China plastics machinery was Thailand 6.6% (-40.8%), Indonesia 5.3% (+22.3%), Iran 4.7% (+14.9%), Japan 4.6%, Turkey 3.6%, Korea 3.4%, and Mexico 3.3%. The top 10 export destination for Chinese plastics machinery accounted for 51% of China plastics machinery total exports. This indicates that China's exports are not concentrated at certain regions.
4.3 Japan Export Status
Japan is one of the major exporting countries for plastics machinery in Asia. 20 years ago, the Japanmade machinery were still dominating the market, but the growing market share from Taiwan, Korea, and China has put much pressure on Japanese manufacturing. In 2016, the total value of Japanese machinery was USD 2.1 billion, increased 1.1% from its previous year and ranked the third globally.
The top market for Japanese machinery exports in 2016 was China, with total value of USD 608 million, increased 7.3%, and accounted for 28.4% of its total exports. The USA was the second largest destination, with USD 389 million, increased 0.5%, and accounted 18.2%. Korea was the third largest destination, with USD 147 million and increased 4.3%.
The rest were Thailand 6.0% (-27.0%), Vietnam 3.8% (-22.8%), Indonesia 3.8% (-5.8%), Mexico 3.7% (+18.1%), India 3.0%, Taiwan 3.0%, Malaysia 2.4%. The top 10 destinations counted up to 80% of its overall exports.
4.4 Italy Export Status
Italy is an important exporter in contributing to worldwide plastics machinery production and exports. It used to be the second largest exporter after Germany; however, it is losing market share partially due to the strong Euro against USD. In recent months, Euro exchange rate has lowered and this has profited Italian machinery and regained its competitiveness. In 2016, Italian machinery ranked the fourth, total value of USD 2.1 billion and decreased 0.7%.
Italian plastics machinery top export was to the USA, with total value USD 185 million, decreased 17.7%, and accounted 8.7%. The second largest destination was to Germany USD 155 billion, decreased 6.7%, and accounted 7.3%. The third was to Mexico, increased 67.2%, and accounted 6.7%.
The rest were China 5.4% (+1.7%), Spain 5.0% (+23.7%), France 4.5% (-4.6%), Poland 4.2% (+12.5%), UK 3.9%, Turkey 3.7, and India 2.8%. The top 10 destinations accounted 50% overall export.
4.5 USA Export Status
The USA was the second largest producer compared to Europe and Asia. In 2016, its total value of exports reached USD 1.6 billion, ranked in fifth place and increased 0.8% compared to its previous year.
The top export was to Mexico, with USD 399 million, increased 32.5%, and accounted 24.6% of market share. The second largest was to Canada, with total value of USD 307 million, decreased 2.4%, and accounted 18.9%. Germany was the third, with total value of USD 164 million, increased 4.0%, and accounted 10.1%.
The rest was China 5.5% (-29.2%), Korea 3.0% (3.8%), UK 2.3% (-9.9%), India 2.0%, Japan 1.9%, Singapore1.5%, and Saudi Arabi 1.5%. The top 10 destinations accounted 71% of its all market share.
4.6 Taiwan Export Status
Taiwan is one of the most important exporting countries to the global industry, with showcasing as a large pavilion at some of the most important exhibitions worldwide like Germany’s K show, China’s Chinaplas, Japan's IPF, USA's NPE, and Italy's PLAST. Also, the TaipeiPLAS from Taiwan is also a globally renowned show to the global industry. Taiwan exported a total of USD 1.0 billion, which decreased 8.0% and ranked sixth worldwide.
The top market for Taiwan exports in 2016 was to China, with a total value of USD 195 million, decreased 12.5%, and accounted for 28.2% of Taiwan's total exports. The second largest export was to Vietnam, with total value of USD 136 million, increased 11.3%, and accounted for 13.2% of total exports. The third was to Indonesia, with a total value of USD 70.9 million, decreased 11.9%, and accounted 6.9%.
The rest was Thailand 6.2% (-2.9%), India 6.0% (+6.6%), USA 5.5% (-32.1%), Japan 4.7%, Malaysia 2.8%, Turkey 2.4%, and Mexico 2.3%. The top 10 destinations accounted up to 69% over all of Taiwan plastic machinery export
5. Question and Prospect
Roughly 85-90% of worldwide production comes from Germany, China, Japan, Italy, USA, and Korea. In 2015,the global total production value of plastic machinery reached Euro 29 billion. Among all producing countries,
Germany produced Euro 7 billion, China produced Euro 8.6 billion, Italy produced Euro 2.5 billion, USA produced Euro 1.9 billion, Japan produced Euro 1.8 billion, and Taiwan produced Euro 1.6 billion.
When looking at exports, Germany, China, Japan, Italy, USA, and Taiwan accounted for 80% of all exports. In
2016, Germany exported USD 5.5 billion, China exported USD 3.5 billion, Japan exported USD 2.1 billion, Italy
exported USD 2.1 billion, USA exported USD 1.6 billion, and Taiwan exported USD 1.0 billion.
The worldwide plastics machinery exports are still majorly from Europe and Asia, especially now that Asia
is experiencing a high increase in industrial growth. It is expected that Asia will become the worldwide production hub for the world, where the demand for plastics machinery is still high.
5.1 China and ASEAN still accounts for around 50% of all Taiwan exports. Taiwan should reduce the risk and distribute to other markets as well
The biggest problem that the Taiwan plastics machinery industry is currently facing is the over concentration on China and South-East Asia markets. Currently, China accounts for 19% of all Taiwan plastic machinery exports, and South-East Asia with 30%.
There are some other new developing markets worthwhile for Taiwan to explore, such as India, Egypt, Iran, Saudi Arabi, South Africa, Mexico, Bengal, Brazil, Argentina, Poland, and Russia. Currently, the middleeast and near-east regions account for 7.1% of all Taiwan plastic machinery exports, Africa 6.3%, Central and
South America 6.3%, and central Europe 1.9%. All these above countries are still worth while for Taiwanese manufacturers to develop, exhibit, and explore for new market potential.
5.2 All electric models will become the major trend and are worth researching
Fully electric machines have good advantages with zero oil pollution, low noise, low vibration, and it even saves electricity, cooling water, and operational costs. Therefore, the high-tech industries like computer-making, electronic, multi-media, communication, mobile, and optical manufacturing are more willing to consider fully electric models as priority. In 2016, Taiwan imported 1,050 injection molding machines. These machines were worth a total value of USD 58.5 million, which Japan machinery accounted 402 machines, total value of USD 33.8 million. These machines mark an average of USD 84.1 thousand per machine, which is 1.83 times more than Taiwan’s average of USD 45.9 thousand. Among all injection machines being imported to Taiwan, Japan accounted 57.8%, China accounted 22.6%, and Germany accounted 5.8%, showing that Japanese-made injection molding machines still dominate the Taiwan market. Taiwan should be urged to set clear directions for developing fully electric models.
From the data shared by Japan Plastic Machinery Association, roughly 80% of all injection-molding machines are fully electric models. The industry critics have even predicted that over 70% of 1,600 ton or smaller injection molding machines from Japan, Europe, Northern America will be fully electric models 10 years from now. Other advantages of fully electric models are that the standard injection molding machines can achieve 300 mm/sec and high-speed models can even reach up to 1,000 mm/ sec, and this new model also deliver short forming cycles. There is no doubt that the fully electric models will be widely used in high-tech, medical, precision manufacturing, and in other industries.
5.3 New generation of plastics machinery should focus on new applications for key components and developing automated plastics machinery
(1) The application of servo motor and inverter
The servomotor and inverter may replace the complex structure in the machines, especially for energy savings. Also facing the difficult problem on producing and fixing precision component, servo motor and inverter may be an answer to overcome such problems.
(2) Full utilization of European key components
While plastics machinery production and assembly is now all happening in Asia, the precision key components are still produced in Europe. This cooperation will help maintain machines of high quality, remaining at a lower cost, and create a win-win situation.
(3) Automation, customization, and Smart machines are just around the corner
To solve for the lack of labor and the increased labor costs, the demand for automated machinery is without doubt to be highly emphasized. This results in the ending of operator requirements for processing on each machine. In the future, it may only require one supervisor to run multiple machines on the production line. Also, there is an increasing demand for low-quantity, high-value customized production, which may further boost the coming era for customized manufacturing and industry 4.0 smart manufacturing.
Taiwan manufacturers now also are producing for fullye lectric models. At the next TaipeiPLAS in August 2018, there will be much more fully electric machines presented at the show from Taiwan companies. In the future, Taiwan will also move forward and develop for low tonnage, fully electric injection molding machines. Another highlight at the show will emphasize new solutions for smart plastic injection molding.
The Japanese and German producers for control panel and servomotor are also expecting these new trends that have been cultivated in Taiwan, and they wish to support with their key components to further boost and fully transform the Taiwanese plastics machinery industry towards fully electric models.
Injection molding machines from Japan, Europe, Northern America will be fully electric models 10 years from now. Other advantages of fully electric models are that the standard injection molding machines can achieve 300 mm/ sec and high-speed models can even reach up to 1,000 mm/ sec, and this new model also deliver short forming cycles. There is no doubt that the fully electric models will be widely used in high-tech, medical, precision manufacturing, and in other industries.
6.3 New generation of plastics machinery should focus on new applications for key components and developing automated plastics machinery
(1) The application of servo motor and inverter
The servomotor and inverter may replace the complex structure in the machines, especially for energy savings.
Also facing the difficult problem on producing and fixing precision component, servo motor and inverter may be an answer to overcome such problems.
(2) Full utilization of European key components
While plastics machinery production and assembly is now all happening in Asia, the precision key components are still produced in Europe. This cooperation will help maintain machines of high quality, remaining at a lower cost, and create a win-win situation.
(3) Automation, customization, and Smart machines are just around the corner
To solve for the lack of labor and the increased labor costs, the demand for automated machinery is without doubt to be highly emphasized. This results in the ending of operator requirements for processing on each machine. In the future, it may only require one supervisor to run multiple machines on the production line. Also, there is an increasing demand for low-quantity, high-value customized production, which may further boost the coming era for customized manufacturing and industry 4.0 smart manufacturing.
Taiwan manufacturers now also are producing for fully electric models. At the next TaipeiPLAS in August 2018, there will be much more fully electric machines presented at the show from Taiwan companies. In the future, Taiwan will also move forward and develop for low tonnage, fully electric injection molding machines. Another highlight at the show will emphasize new solutions for smart plastic injection molding.
The Japanese and German producers for control panel and servomotor are also expecting these new trends that have been cultivated in Taiwan, and they wish to support with their key components to further boost and fully transform the Taiwanese plastics machinery industry towards fully electric models.
